Blockchain
- Prakul Neupane
- Jun 7, 2020
- 4 min read
Updated: Nov 10, 2022
Hello!
Welcome to my blog for my YouTube channel, Stick2Tech!
Today we will be talking about Blockchain.

First, Blockchain is like a series of blocks, which could contain data for a transaction, messages, or instructions for machines. The information from the Blockchain is recorded by nodes. I will go into detail about these terms below.
1. Block

There are three parts of blocks, the data, which is whatever is being transferred in the Blockchain, the hash; for more details on Hashes, please watch my previous video on the subject; and a hash pointer, which is used to show when the data from a previous block is referenced.
2. Blockchain
The above picture shows the Blockchain when a block points or references a previous block’s hash key. The next picture above shows an example of how the hash key helps to create a Blockchain.
3. Peer-to-Peer (P2P) Nodes
Blockchains are managed by peer-to-peer nodes. Nodes are a series of servers that store data for Blockchains. If a new block is added to one server in the peer-to-peer network, it will be replicated to other peers with consensus. That means they have to verify that the block added is good before adding it to the other nodes.
You can click on the pictures above to see the flow when a block is added to a block and how it gets consensus before being added to other nodes.
4. Security
There are three security measures that prevent this information from being tampered with by malicious nodes:
a. Hash Pointers
First is the hash pointers. If data in block two is tampered with, it will have a different hash number, meaning blocks three and any other following blocks will be invalid because they no longer reference the original hash key. The flow of the broken chain can be seen by clicking through the picture.
b. Proof of work
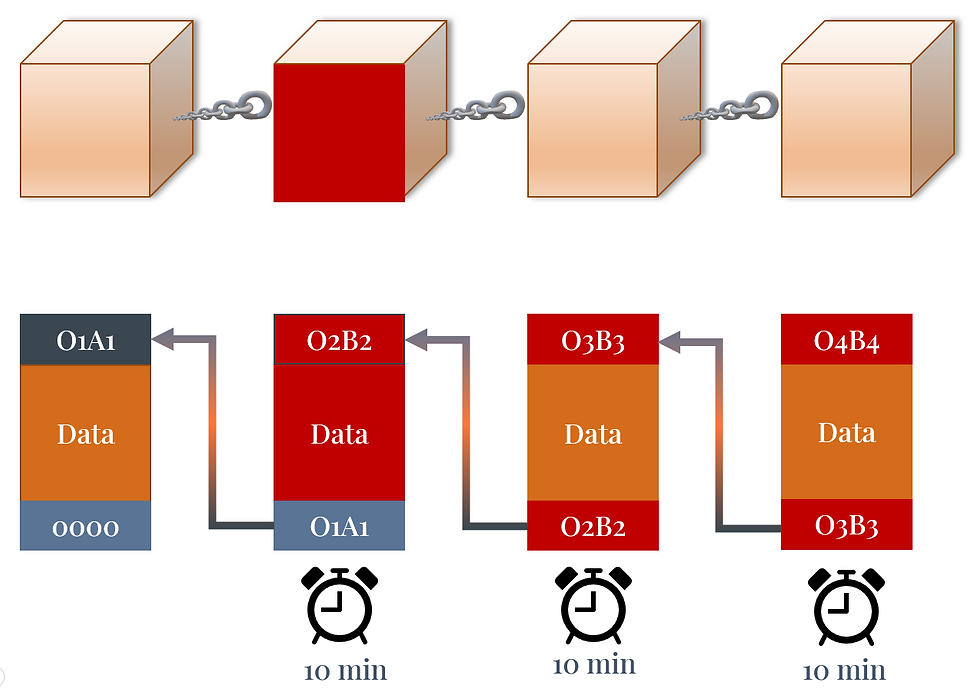
The second is Proof of work. This is to make sure that they don’t tamper with all of the following blocks to reference the new hash key. It takes 10 minutes to add a new block to a chain, so the hackers need to change all of the references in such a short time frame so that one of the nodes doesn’t recognize something is wrong in the 10-minute delay of every change.
b. Peer to Peer consensus
Finally is Peer-to-peer consensus, which allows different nodes across the internet to look at the information and check it to make sure the information is consistent. If the information is not consistent in that node, it will be deemed a malicious node.
In the example above, Node "A" has data tampering. Other nodes found the information inconsistent and deemed Node "A" malicious. The tampered data are not replicated to other nodes.
5. Examples
a. Example - Monetary Transaction
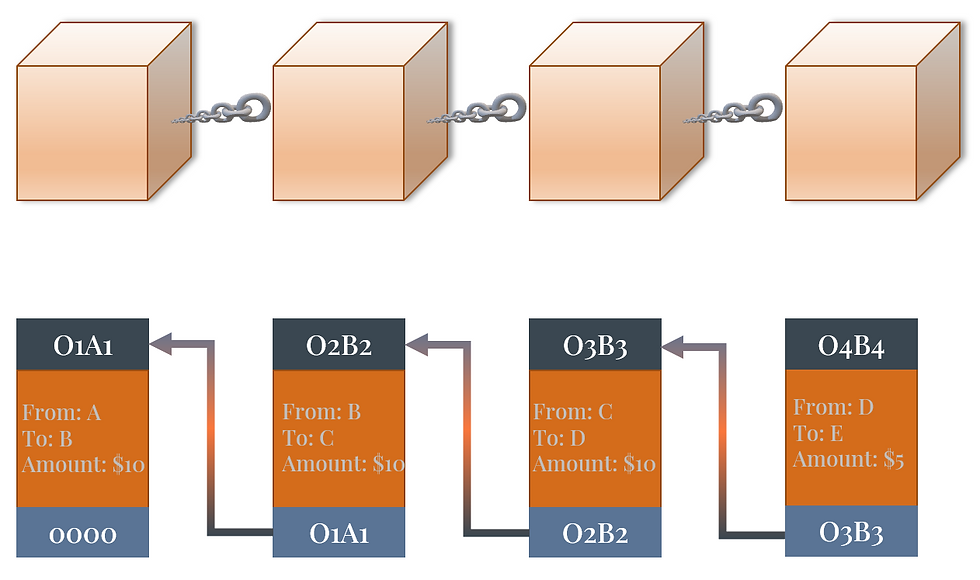
The first example of Blockchain use is on transactions. It is used so that the transactions are kept in a ledger, and each transaction is recorded as a new block in decentralized nodes. This prevents any tampering with the original transactions and speeds up the verification process in distributed systems because of the security measures listed above.
a. Example - Supply Chain (Organic Milk)
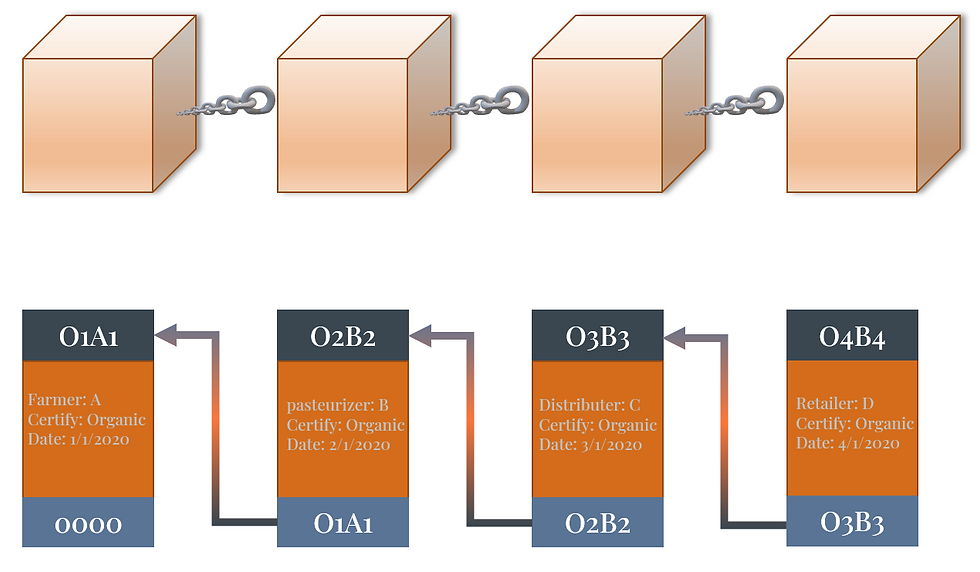
Another use of Blockchain could be in supply chains. For example, for organic milk to be brought from the farmer to the store, it needs to record each level of the supply chain, from pasteurization to distribution. Identified for example, if someone gets sick from that product., they need to know every level of the supply chain to make sure the USDA knows all parties involved to verify their practices and see if this could lead to more health violations.
This example can be for other industries like the diamond industry, where many parties are involved in the extraction and refinement of diamonds. Therefore many parts of the supply chain may have to be recorded in the Blockchain.
6. Benefits

Some benefits of using Blockchain have improved accuracy by removing human involvement in verification, cost reductions by eliminating third-party verification, decentralization that makes it harder to tamper with, and transactions that are secure. It has private, efficient, and transparent technology.[1]
7. Shortcomings

However, there are shortcomings to using Blockchain, including a significant technology cost associated with mining bitcoin, low transactions per second because of proof of work, history of use in illicit activities, and susceptibility to being hacked.[1]
Thank you for reading my presentation about Blockchain, I will be making other videos relatively soon, and I want to hear your opinion about what I should talk about. Should I go more in-depth with this topic, or is there something you want specifically? If this topic interests you, I encourage you to do your research on the subject.
Thank you for reading my Blog about Blockchain, I will be making other blogs relatively soon, and I want to hear your opinion about what I should talk about. Should I go more in-depth with this topic, or is there something you want specifically, like Cryptocurrencies in relation to Blockchain? If this topic interests you, I encourage you to do your own research on the subject or write in the comments below if you have any questions for me.
Acknowledgments:
[1]https://www.investopedia.com/terms/b/blockchain.asp
[2]https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SSo_EIwHSd4
[3]https://www.cs.unm.edu/~saia/classes/591-Blockchains-s19/lec/lec1-crypto.pdf






















Comments